

The laws of reflection are valid for all. Angle AMO and NMB' are vertical angles and vertical angles are congruent. The incident ray is a ray from the light source incident on the plane mirror. Laws of reflection: it states that, if a light ray is reflected from a plane flat polished surface its angle of the incident will always be equal the angle of reflection i.e., The angle of incidence ( i ) Angle of reflection ( r ) Incident ray, reflected ray, normal all lies on the same plane. The way that light bounces off the surface of an object follows a strict law called the Law of Reflection, which says The angle of incidence equals the.
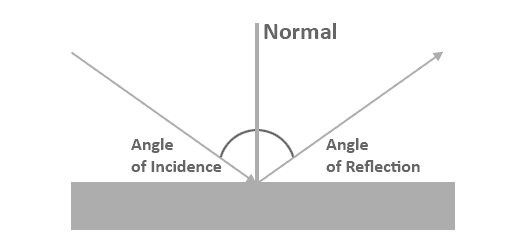
To understand reflection using the ray model, we need to first define certain terms. However, when analyzing the behavior of light using the ray model, we use just one, two, or three rays to show the path of the rays and image formation. When light reflects from a smooth surface such as that of metal or glass or water, the incoming angle of incidence is equal to the outgoing angle of reflection. There are numerous rays coming from a single source. Nearly all of the light is reflected back. A plane mirror is a highly polished surface with minimal absorption or refraction of light. Discussion of Principles Reflection by a Plane Mirror When light is incident on a surface, some of the light is reflected back while some of it is transmitted or absorbed. Now you have many electrons that are being bombarded by even more photons, all emitting photons in many directions. The law of reflection states that when a ray of light reflects off a surface, the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Lets assume that the beam of light hits the reflecting surface directly from above, so the angle of incidence is 0 degrees. In this experiment, you will examine how light rays behave due to reflection and refraction in plane surfaces. Hint: this is where the wave nature of light comes into play. When these rays encounter a mirror, lens, or prism, for example, they bend or change direction. In geometric optics light is represented as rays coming from a light source. Lenses and mirrors are the basic components of many common optical devices such as cameras, telescopes, eyeglasses, binoculars and microscopes. Image formation by lenses and mirrors is explained by these two laws.
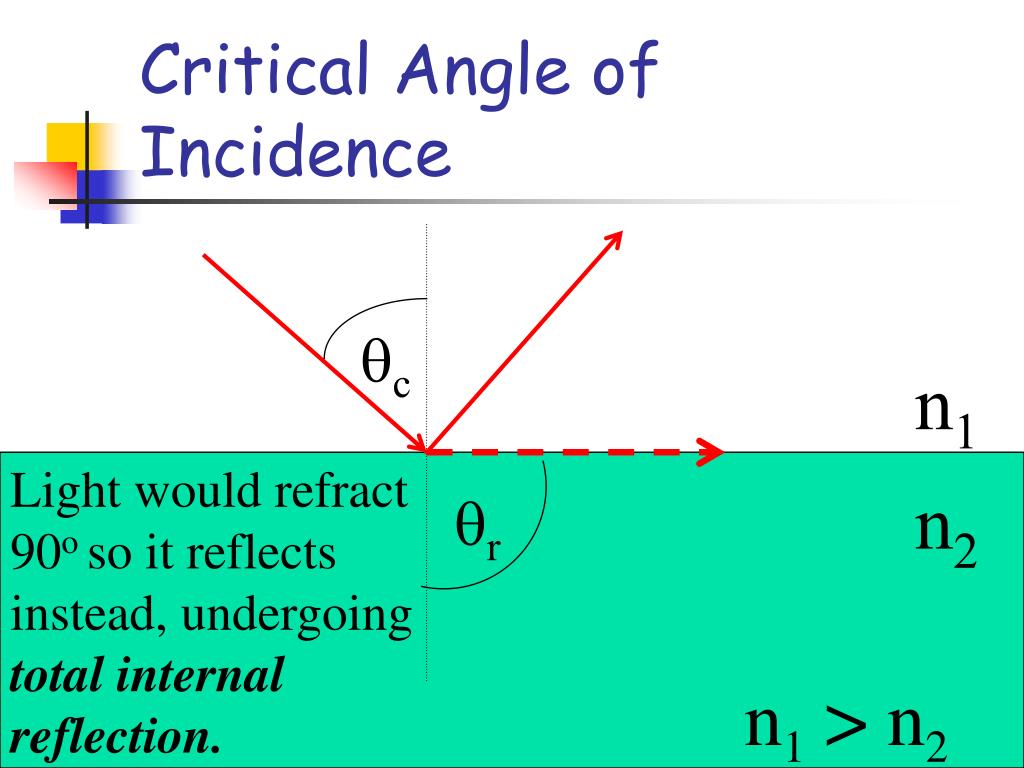
The law of refraction, however, was not formulated mathematically until almost 1500 years later. The law of reflection was known to the ancient Greeks who made measurements that supported this law. Lab 10 - Reflection and Refraction Introduction Geometric optics is one of the oldest branches of physics, dealing with the laws of refraction and reflection.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
